Before we can proceed, you need to refer to this post to create 2 RDP listeners. Once you have multiple RDP listeners, the first step we need to do is to open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration. You can do it by typing tsconfig.msc from run. As you can see in the screen captures below, there are actually 2 connections.
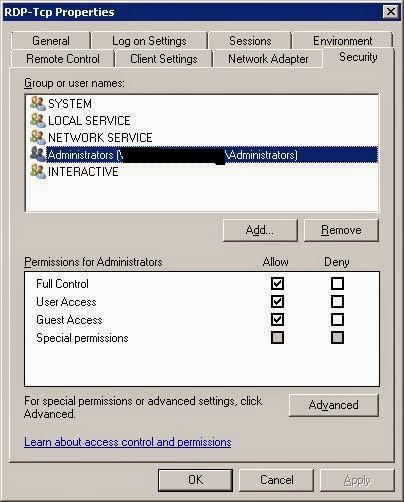
Assuming RDP-Tcp allow drive redirection and only Administrator can use it while RDP-Tcp-normalUser does not allow drive redirection and user1 can use it. So click on RDP-Tcp-normalUser and change the following:
Add in user1
Configure drive redirect, for this example, i disable all Redirection features.
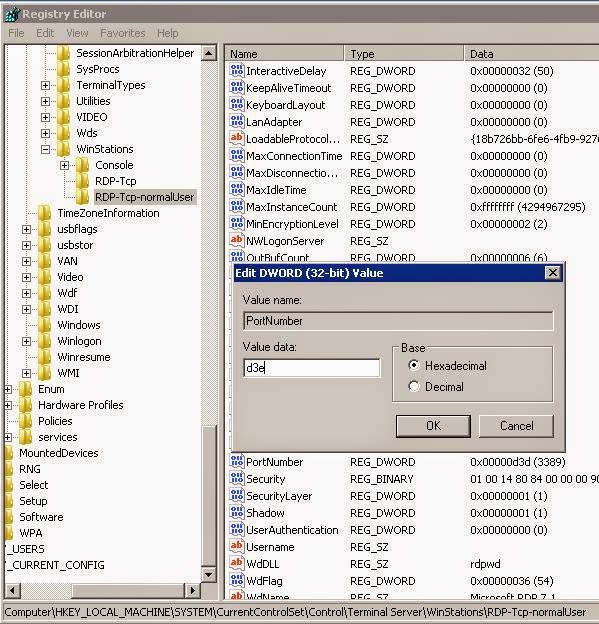
Click on RDP-Tcp and make sure no user1 in this profile.
From client, you can do drive redirection by go to Local Resources tab and click More
A new Window let you select which drive to redirect
So if you login using Administrator with the default connection (default port 3389), you should see the mapped drive under Others.
If you login using user1 with the new connection (port 3390), you should not see any mapped drive.
Assuming RDP-Tcp allow drive redirection and only Administrator can use it while RDP-Tcp-normalUser does not allow drive redirection and user1 can use it. So click on RDP-Tcp-normalUser and change the following:
Add in user1
Configure drive redirect, for this example, i disable all Redirection features.
Click on RDP-Tcp and make sure no user1 in this profile.
From client, you can do drive redirection by go to Local Resources tab and click More
A new Window let you select which drive to redirect
So if you login using Administrator with the default connection (default port 3389), you should see the mapped drive under Others.
If you login using user1 with the new connection (port 3390), you should not see any mapped drive.